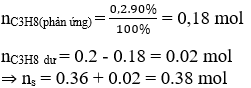C reaction3H8 (propane) or C3H8 out ONLY4 (methane) and C2H4 (ethylene) As one of the cracking reactions, the following article elaborates on the reactants, balanced chemical equations and some common Cracking reactions.
1. Composition of substances in the reaction:
1.1. What is propane?
C3H8 is the chemical formula of Propane or gas propane. This is an open-chain, saturated hydrocarbon compound with a molar mass of 44g/mol.
At standard temperature and pressure conditions, propane exists as a gas. Furthermore, it can be compressed into liquid propane for easy transportation and storage.
Propane is a by-product of natural gas processing and oil refining. They are therefore often used as fuels for thermal applications.
C3H8 is stored and stored at the same pressure as the liquid in propane cylinders. Therefore, it is easy to return to vapor form when you release the pressure level in the air tank.
The equation to make C3H8 (Propane):
2H2 + OLD3H4 → OLD3H8
H2 + OLD3H6 → OLD3H8
ONLY3Cl + 2Na + OLD2H5Cl → 2NaCl + OLD3H8
1.2. What is methane?
– In nature, methane is abundant in gas fields (natural gas), in oil fields (oil field gas), in coal mines (coal mine gas).
Methane has a molecular formula of CH4 and molecular mass is 16 units.
Methane is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas that is lighter than air. The density of methane to air is dCH4/kk = 16/29. Methane is very slightly soluble in water. It liquefies at −162 °C, solidifies at −183 °C, and is highly flammable.
– Methane is an important material in life and production because when it burns it produces a large amount of heat. As the raw material to make H2: ONLY4 + FRIENDS2O (t°, xt) → CO2 + FRIENDS2
– Methane is a raw material for the preparation of coal powder and many other substances such as methanol, acetic acid, acetic anhydride…
Equation to generate ONLY4 (methane):
OLD + 2H2 → ONLY4
2NaOH + ONLY2(COONa)2 → ONLY4 + 2Na2CO3
Catalysis: High Other conditions: high temperature
ONLY3COONa + NaOH → ONLY4 + Na2CO3
Temperature: temperature Catalysis: High
1.3. What is ethylene?
Ethylene has the molecular formula: C2H4 and has molecular mass: 28 unitsC
Ethylene is a gas, colorless, odorless, lighter than air and sparingly soluble in water.
Similar to methane, when burning ethylene gas, it produces CO . gas2steam and give off a lot of heat.
– Ethylene is used to prepare acetic acid, ethyl alcohol, poly (vinyl chloride), …
– Ethylene is used to stimulate fruit ripening.
Equation to generate OLD2H4 (ethylene):
OLD2H6 → OLD2H4 + H2
Temperature: 500°C Catalysis: catalysis
OLD2H5OH → OLD2H4 + H2O
Temperature: 170°C Catalysis: H2SO4
OLD2H5Cl → OLD2H4 + HCl
Solvent: dd NaOH / C2H5OH
2. Conditions for the reaction to occur:
– High temperature.
– Catalyst: Ni, Fe, Cr2O3PT…
Under the effect of high heat and suitable catalyst C3H8 can be decomposed into ONLY4 and C2H4
– Identification: Lead the product mixture obtained through the container of Bromine solution to see that the Bromine solution is pale.
3. Cracking reaction:
– The above reaction is called cracking reaction4 and C2H4 The resulting product may have both2 and C3H6.
– Under conditions of high temperature, pressure and catalysis, alkanes can break the C chain to form smaller alkanes and alkenes called cracking.
– Regardless of which direction the reaction takes place, the reaction does not change the mass of the mixture: mbefore reaction = mafter reaction.
– The reaction always increases the number of moles of gas: nafter > nbefore
– Some common cracking reactions
Butane cracking reaction C4Hten
When performing butane cracking reaction, a mixture of alkanes and alkenes will be obtained such as: C4H8H2ONLY4,3H6,2H6,2H4…
Reaction Equation:
OLD4Hten → OLD4H8+ FRIENDS2
OLD4Hten→ ONLY4 + OLD3H6
OLD4Hten → OLD2H6+ OLD2H4
OLD4Hten → OLD3H8 + ONLY2
– Method of solving the Cracking Ankan exercise:
Under the effect of temperature, catalyst, alkanes can react in many directions:
Cracking reaction: ANKAN −tº, xt→ OTHER ANKAN + ANKEN (discolors dd bromine)
Dehydrogenation reaction: ANKAN −tº, xt→ ANKEN + FAMILY2
For example:
OLD3H8 −tº, xt→ ONLY4 + OLD2H4 (ONLY2= ONLY2)
OLD3H8 −tº, xt→ OLD3H6 (ONLY2=CH–JUST3) + FAMILY2
In particular, under the right conditions, the reaction can also:
+ Generate alkines: For example: 2CH4 −1500ºC, lln→ ONLY + 3 HOURS2
+ Generate carbon and hydrogen: Example: ONLY4 −tº, xt→ C (solid) + 2H2
The reaction does not change the mass of the mixture:
mbefore reaction = mafter reaction MOTHERD/MOTHERS = nS/nD
the content of C and H before and after the reaction is the same ⇒ the combustion of the mixture after the reaction is referred to as the combustion of the mixture before the reaction.
– The reaction always increases the number of moles of gas: nafter > nbefore Pafter > Phead MOTHERtb after < CODEtb head (because mhead = mafter)
Example:3H8 −tº, xt→ ONLY4 + OLD2H4 nsau = 2. First
– Number of moles of alkenes produced: nalkenes = nS – nD; Reaction efficiency: H = (nS– nD)/nD .100%
4. Related exercises and instructions:
1. Cracking3H8 obtain a mixture X consisting of H2,2H4ONLY4,3H6,3H8 has dX/He = 10. The reaction efficiency is:
A. 10%
B. 80%.
C. 70%.
D. 60%
Instruct.
Cracking C3H8:
C3H8
CH4 + C2H4
x x x mole
C3H8
H2 + OLD3H6
y y y mol
We see in X remaining 1 part C3H8 not cracked yet.
USAX = USHe.10 = 4.10 = 40 g/mol
Assume there is 1 mole of C3H8.
Conservation of mass has: mbefore = mafter or 1.44 = nx.40 → nx = 1.1 mol
According to the high school with nC3H8p = nafter – nbefore = 1.1 – 1 = 0.1 mol
So
Answer: A
2. ONLY4,2H4,3H6 and partially uncracked propane. Know the reaction efficiency is 90%. The average molecular mass of A is:
A. 39.6
B. 23.16
C. 2,315
D. 3.96
Instruct.
Cracking C3H8:
OLD3H8 → ONLY4 + OLD2H4
OLD3H8 → FRIENDS2 + OLD3H6
It can be seen that for every 1 mol C . loss3H8 will form 2 moles of product. ScreenC3H8 = 0.2 mol
Efficiency H = 90%
⇒ number of moles sp formed is: 0.2.90%.2 = 0.36 mol;
3. ONLY4,2H4,2H6 and partially uncracked propane. Complete combustion of A yields 9 grams of H2O and 17.6 grams of CO2. The value of m is:
A. 4.4g
B. 6.6g
C. 8.8g
D. 11g
Instruct
The product of combustion of A is similar to that of propane
npropane = nH2O – nCO2 = 9/18 – 17.6/44 = 0.1 mol
mpropane = m = 0.1.44 = 4.4 grams
Answer A.
4. The general formula of alkanes is
A. OLDnHn+2
B. OLDnH2n+2
C. OLDnH2n
D. OLDnH2n-2
The answer is NO
5. Number of structural isomers corresponding to the molecular formula C5HtwelfthTo be
A. 6
B. 4
C. 5
D. 3
Instruct:
Alkane isomers with CTPT C5Htwelfth To be:
ONLY3– ONLY2– ONLY2– ONLY2– ONLY3
ONLY3-CH(ONLY3)-ONLY2– ONLY3
C(ONLY3)4
So there are 3 isomers in all.
EASY ANSWER
6. Number of structural isomers corresponding to the molecular formula C6H14 To be
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6.
Instruct:
Write structural isomers of C6H14
ONLY3– ONLY2– ONLY2– ONLY2– ONLY2– ONLY3
ONLY3-CH(ONLY3)-ONLY2– ONLY2– ONLY3
ONLY3– ONLY2-CH(ONLY3)-ONLY2– ONLY3
(ONLY3)2-CH-CH(ONLY3)2
(ONLY3)3-C-ONLY2– ONLY3
Thus c6H14 There are 5 structural isomers.
Answer:
7. Compounds (ONLY3)2ONLY2ONLY2ONLY3 whose name is
A. neopentan
B. 2- methylpentane
C. isopentan
D. 1,1- dimethylbutane.
Answer: REMOVE
8. Alkanes (ONLY3)2ONLY2C(ONLY3)3 whose name is
A. 2,2,4-trimethylpentane
B. 2,2,4,4-tetramethylbutane
C. 2,4,4-trimethylpentane
D. 2,4,4,4-tetramethylbutane
Answer: A
9. Alkanes X has the molecular formula C5Htwelfth. Chlorination of X yields 4 monochlorine derivatives. X’s name is
A. 2,2-dimethylpropane
B. 2- methylbutane
C. pentan
D. 2- dimethylpropane
Answer: REMOVE
10. Complete the following reaction diagram (write the condition of the reaction)
C3H8 -> CH4 -> C2H2 -> C2H4 -> C2H6 -> C2H5Cl
Answer:
(1) C3H8 -> C2H4 + CH4
(2) 2CH4 -> C2H2 + 2H2
(3) C2H2 + H2 -> C2H4
(4) C2H4 + H2 -> C2H6
(5) C2H6 + Cl2 -> HCl + C2H5Cl
11. Cracking butane yields 35 mol hh A consisting of ONLY4,2H6H2,2H4,3H6,4H8 and C4Hten residual. Walk A through a flask of excess bromine water and see that 20 moles of gas come out of the flask (knowing that only C2H4,3H6,4H8 Reaction with Br2 and in a 1:1 molar ratio). If A is completely burned, a mole of CO . is obtained2.
a. Calculate the yield of the reaction that produces hh A.
b. Calculate the value of a.
Prize:
a. Reaction Equation:
OLD4Hten −tº, xt→ ONLY4 + OLD3H6
OLD4Hten −tº, xt→ OLD2H6 + OLD2H4
OLD4Hten −tº, xt→ FRIENDS2 + OLD4H8
Number of moles of alkenes obtained: nalkenes= 35 – 20 = 15mol
The initial number of moles of butane is: nD = nbutane = nS – nalkenes = 35 – 15 = 20 mol
So butane cracking efficiency is H = (nS– nD)/nD .100% = (35-20)/20.100% = 75%
b. Combustion of mixture A is burning butane:
OLD4Hten + 11/2O2 → 4CO2 + 5 HOURS2O
20 80 mol
So the number of moles of CO2 obtained by burning mixture A is 80 mol